

The distal neurological examination of the right upper extremity and distal pulses was intact and was compared to the contralateral limb.
#Ao classification of galeazzi fracture full#
The right elbow, metacarpophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints showed a full painless range of motion. The range of motion examination of the wrist was painful and showed a 30° flexion-extension arc and 60° of pronosupination. Local examination of the right forearm showed an obvious deformity with minimal tenderness to palpation. Examination: On general examination, he was a well-built gentleman that was not in any pain or discomfort. The patient came to us based on the advice of some relatives that he was visiting. The following days the swelling subsided, but the deformity did not resolve completely and he was not able to move his forearm as he could previously, and he did not seek medical attention due to the fact that he was afraid to lose his job.
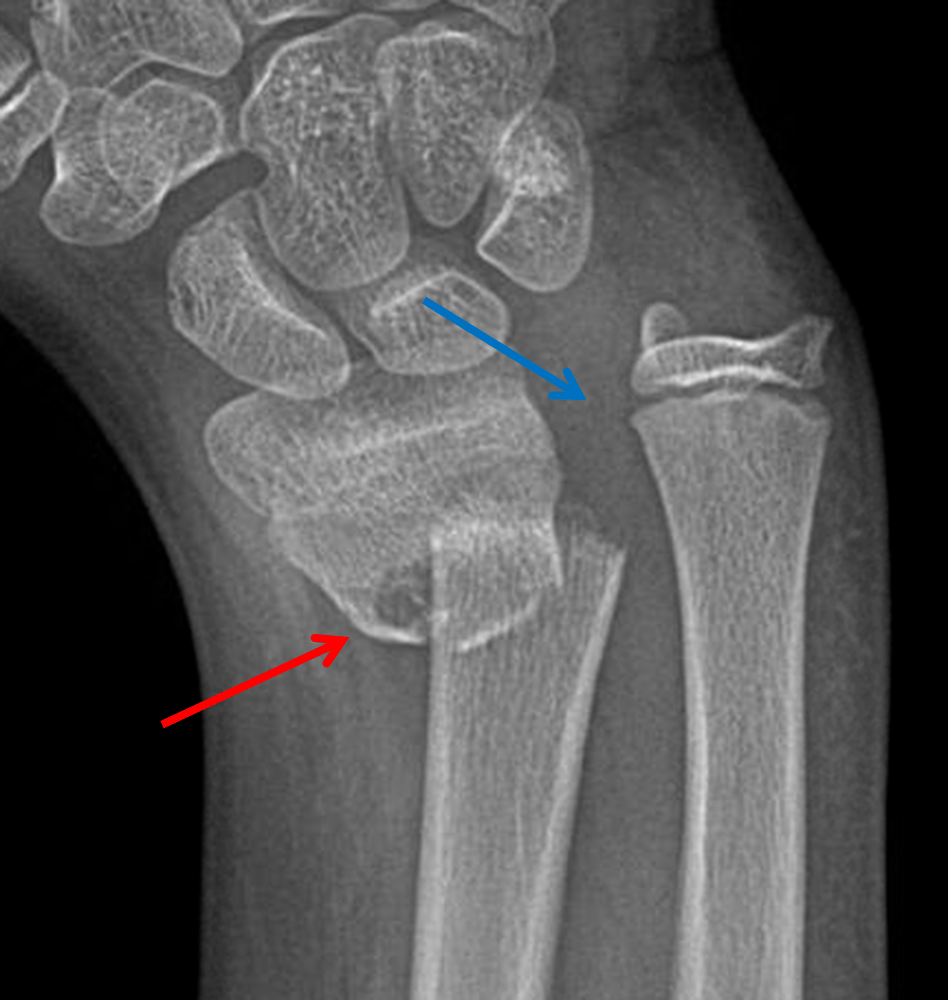
The pain started 72 days back when the patient sustained a road traffic accident and fell from his motorbike on an outstretched hand, since then, he noticed the deformity in his forearm, and he first thought it was a simple contusion or bruise. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations are usually managed acutely due to the apparent deformity, pain, and disability suffered by the patient, we have searched the literature and only found one case reporting a chronic Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, and therefore, we present our experience with this rare injury.Ī 27-year-old man of Eastern Asian descent presented to our outpatient clinic with a complaint of the right forearm pain and deformity for over 2 months. In pediatrics, however, Galeazzi fracture can be amenable to closed treatment with satisfactory outcomes due to several reasons including thick periosteum, stronger ligamentous restraints, and higher bone modeling capacity. Historically Galeazzi fractures is adult were treated with open reduction and internal fixation of the radius fracture with or without DRUJ repair and pinning, the is largely due to the highly unsatisfactory outcomes following closed treatment and chronic disability. On the other hand, two classification systems classify the fracture based on its distance from the DRUJ, the most commonly used is the one by Retting, in which the fracture is either more than 7.5 cm away from the DRUJ or less, the main rationale behind this classification is that fractures < 7.5 cm are more prone to DRUJ instability according to the results of this study. Several classification systems have been proposed for Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, the first was described by Walsh, in which the fracture was classified based on its angulation, the position of the forearm (supination of pronation) on axial loading of the fractures will contribute to its apex (apex volar or apex palmar). The IOM also has a complex structure of bands and cords that prevent translation of the radius and ulna and also transmit axial and rotational forces, the central band is the main restraint and stabilizer within the IOM. Galeazzi fractures are inherently unstable due to the disruption of the DRUJ and possible disruption of the interosseous membrane (IOM), the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is the main stabilizer of the DRUJ and the dorsal and volar radioulnar ligaments are the most important ligaments within the TFCC.
#Ao classification of galeazzi fracture series#
They were first described in 1877 by a British surgeon and then named after Galeazzi who reported a series of cases describing the incidence, mechanism, and treatment of these injuries.

Galeazzi fracture represents a distinct spectrum of forearm injuries that represent approximately 7% of adult and 3% of pediatric forearm fractures, they are a unique injury which involves a fracture of the radial diaphysis, along with disruption or dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
