
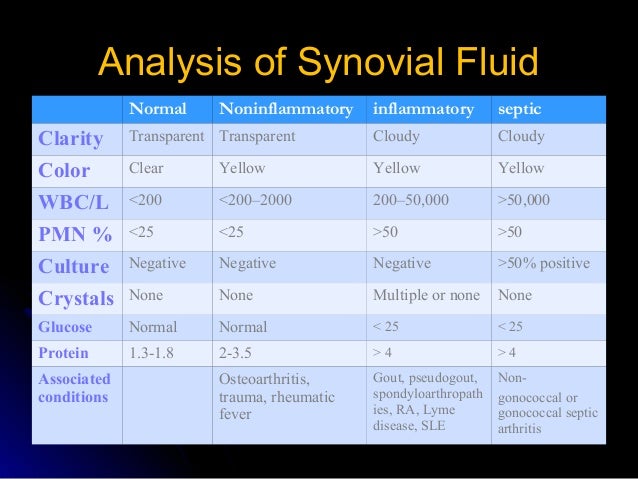
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Serum CRP is commonly used as a screening test for acute infection, but synovial fluid has been found to have a sensitivity and specificity of 92 and 90. Prosthetic joint infection: Epidemiology, microbiology, clinical manifestations and diagnosis. Changes in color, clarity, viscosity, and shifts in the composition of synovial fluid can provide insight and important clinical information on health and disease of the joint.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-joint-effusion-189282_color1-5c1afda046e0fb000176973c.png)
Bacterial arthritis: Clinical features and diagnosis in infants and children. Are there brochures or other printed material that I can take? What websites do you recommend?.Bacteria, a virus or fungus may cause the. The inflammation is in the surface of the cartilage (a type of connective tissue) that lines your joints and the synovial fluid that lubricates your joints. Thus, not even a single definition/test/criterion is conclusive. Septic arthritis (also known as infectious arthritis) happens when an infection spreads to one or more of your joints and causes inflammation. The chief reason being that these patients on cement spacers (after first stage) have smaller amount of synovial fluid and lower WBC thresholds as compared to standard total joint prosthesis. How can I best manage this condition with my other health problems? A Baker cyst forms when an injury or disease causes extra synovial fluid to leak into the extra space behind the knee. The importance of synovial fluid aspiration before reimplantation has been controversial.Usually, the small joints of the hands and feet are affected. Doctors & departments On this page Diagnosis Treatment Preparing for your appointment Diagnosis The following tests typically help diagnose septic arthritis: Joint fluid analysis. Am I at risk of long-term complications from this condition? Typical clinical features of inflammatory joint effusion associated with rheumatoid arthritis include: Symmetrical swollen, warm, erythematous and painful joints.What can I do in the meantime to help relieve my joint pain?.How soon can I expect my symptoms to improve with treatment?.Are there alternatives to the approach you're suggesting?.

Acute and stress-related injuries of bone and cartilage: Pertinent anatomy, basic biomechanics, and imaging perspective.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
